
Payment Services Directive (PSD 2) is a Directive of the European Parliament of 25 November 2015 on payment services within the internal market. Its entry into force will change the current distribution of power on the financial services map and allow for the emergence of independent service providers.
The galloping progress in the area of digitization is lagging far behind modern technology in the current legal framework. It has been 11 years since the adoption of the PSD Directive in the EU and the retail payments market has undergone a major technological revolution. From making payments via mobile phones to completely new non-bank payment methods that are cheaper and more convenient for the consumer.
The aim of the PSD-2 Directive is to regulate and standardize them, which will increase the offering attractiveness on the financial services market.

Online shopping and remote services have become a permanent feature of our lives. The ease and speed of order processing made this form very popular, mainly due to user-friendly mobile applications which are always at hand.
Until now, the financial services sector has been dominated by large financial institutions and traditional approach to transaction execution. The Payment Services Directive 2 will set a new business model in the financial services market. According to the provisions of the Directive, third parties will be able to use the services of banks through a programming interface:
Making those services available to third parties (TPP) by banks is a step toward open banking and a level playing field for entities that have not yet had a chance to participate on this market.
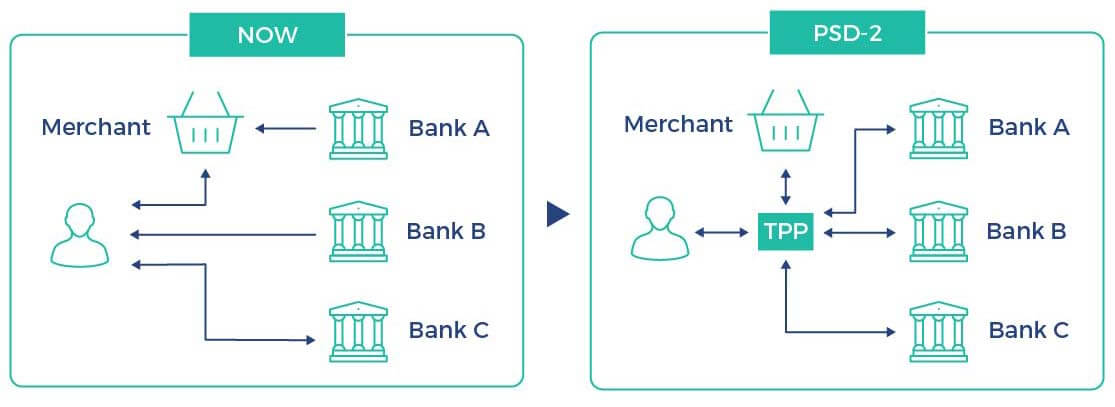
Allowing third parties to carry out transactions will have a positive impact on the competitiveness of the financial sector. It will also stimulate the growth of innovative solutions appearing within the sector itself.
PSD-2 is a level playing field directive that will allow new payment services in the financial segment to develop rapidly in the future. The opening of banking to external service providers will allow for the development of existing solutions and the emergence of new ones. Revival on the services market will have a positive impact on their popularization, which in turn will increase the competitiveness of offers addressed to end customers.
First of all, security of tPro and Payment Services Directive 2
Solutions belonging to the tPro family meet the requirements of the PSD-2 directive in areas such as:
In our offer you will find hardware and software products whose main goal is to ensure security in the processes of transaction authentication and authorization. Technologies developed by us in recent years work successfully for the largest European financial institutions. Our solutions cover all aspects of the PSD-2 regulation.
The PSD2 directive will require payment service providers to use strong customer authentication when accessing financial instruments. The RTS document assumes that user's identity must be verified based on two of the three components, which are knowledge (something the user knows), possession (something the user has) and customer characteristics (something the user is). However, the directive does not remain indifferent to authentication components themselves and requires for them to be independent of each other. This means that the acquisition of one of the components by an unauthorized party does not give them the opportunity to gain access to financial instruments. Applications that meet the requirements of the RTS should be equipped with mechanisms to allow for:
According to the directive, the authentication code assigned to a transaction is explicitly linked to the account number of the payee and the transfer amount. In combination with a secure form of transaction data presentation, a secure method of entering authorization data, real-time monitoring of the launch environment and the encrypted communication with the server, it provides a high level of security and non-repudiation of the transaction.

Authentication data is processed securely at every stage of the authentication code generation, and the cryptographic material itself never leaves the secure memory area of the device. Out of concern for the security of the knowledge component, it is assigned at the stage of application activation (pairing) and is stored in an encrypted memory area. At this stage, user keys are also generated to produce codes to authenticate transactions. The result of this operation is the generation of certificates (trusted CA) confirming who they belong to.
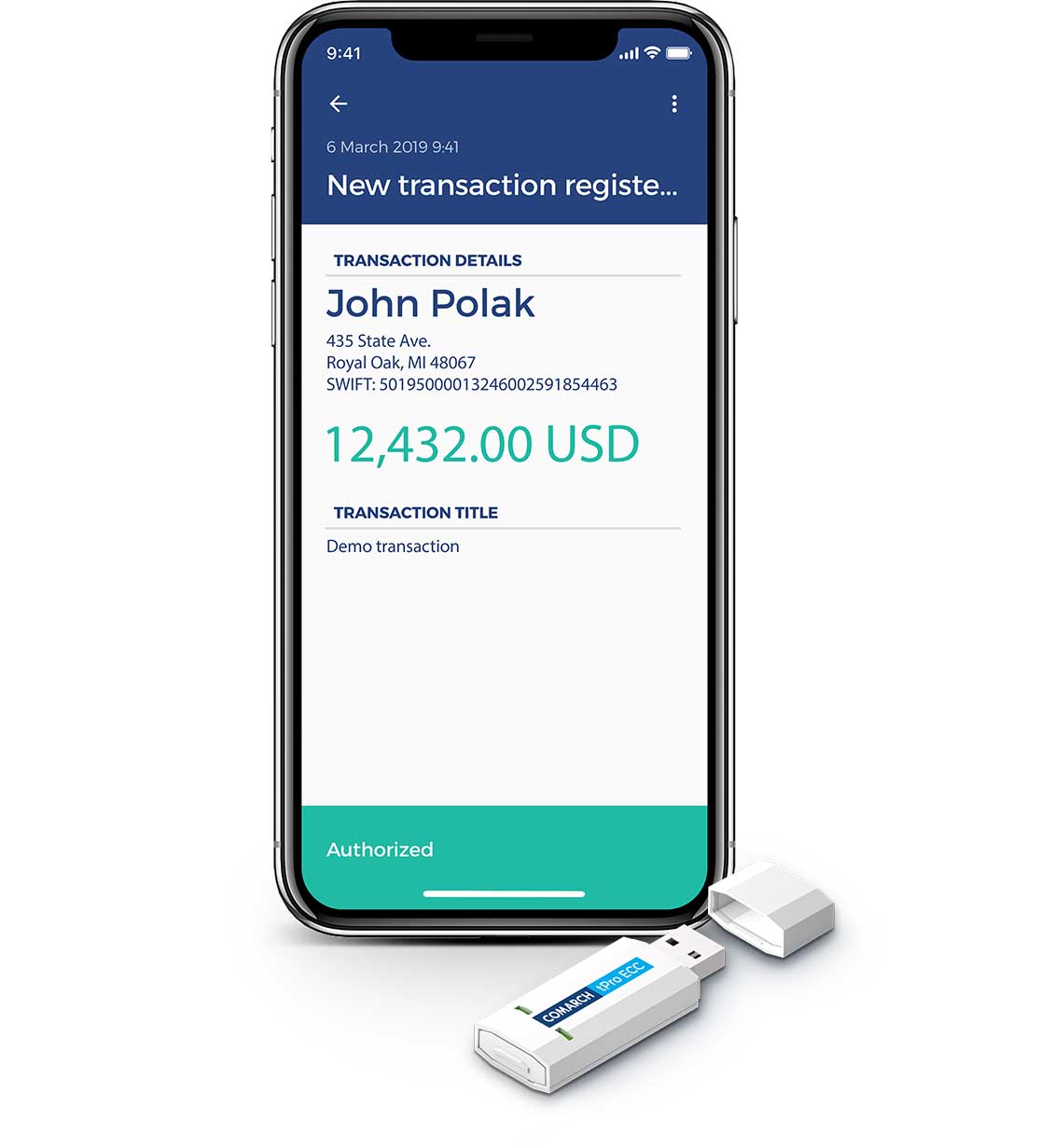
The solutions of the tPro family have been designed to comprehensively implement the provisions of the PSD-2 directive.

Download tPro Solutions leaflet
Read more about how to protect your customers from internet frauds









Tell us about your business needs. We will find the perfect solution.